- What Is NIST?
- What Is Personal Data?
- An Overview of FedRAMP and Why You Should Care About It
- What Is Data Compliance?
- What Is the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)?
-
What Is Healthcare Cybersecurity?
- Why Is Cybersecurity Important to Healthcare
- Elements of Healthcare Cybersecurity
- HIPAA Security Rule
- Healthcare Data Breaches
- Healthcare Business Continuity
- Protected Healthcare Information
- Key Challenges in Healthcare Cybersecurity
- Healthcare Cybersecurity Strategies and Solutions
- The Future of Healthcare Cybersecurity
- Healthcare Cybersecurity FAQs
- What Is GDPR Compliance?
-
What Is HIPAA?
- Is Your Organization HIPAA Compliant?
- Understanding HIPAA
- What Is Protected Health Information (PHI)?
- HIPAA: Breach Notification
- HIPAA Privacy Rule: The Standard of Minimum Necessary
- The Security Rule: Safeguarding Electronic Protected Health Information
- OCR Audit Protocol
- HIPAA for Big Tech and Startups
- HIPAA Compliance Tips for DevOps and AppSec Practitioners
- HIPAA FAQs
- What Is Sensitive Data?
- What Is SOC 2 Compliance?
-
What Is Healthcare Business Continuity?
- Why Is Business Continuity Important to Healthcare?
- Potential Disruptions to Healthcare Organizations’ Continuity
- The Growing Threat of Ransomware in Healthcare
- Why Healthcare Is a Prime Target for Cyberattacks
- How Healthcare Business Continuity Directly Impacts Lives
- Costs of Downtime in the Healthcare Sector
- How to Ensure Business Continuity in Healthcare
- Benefits of Business Continuity Planning
- Healthcare Business Continuity FAQs
- What Are HIPAA Security Rules?
- What Is Protected Health Information (PHI)?
-
What Is Data Governance?
- Data Governance Explained
- Why Data Governance Matters
- The Benefits of Data Governance
- Enterprise Data Governance Challenges
- Cloud Data Governance Challenges
- Data Governance Strategy
- Building a Strong Data Governance Framework
- Data Governance Best Practices: Tips and Strategies
- Securing Data Access: The Importance of Data Access Governance
- Unlock the Full Potential of Your Data with Comprehensive Data Governance Capabilities
- Data Governance FAQs
-
What is the Difference between FISMA and FedRAMP?
-
Simplified Healthcare Compliance and Risk Management with Prisma Cloud
- What Is Data Privacy?
-
How to Maintain AWS Compliance
- What Is Data Privacy Compliance?
- How The Next-Generation Security Platform Contributes to GDPR Compliance
- What Is PCI DSS?
- What Is PII?
What Is Cybersecurity Compliance?
Cybersecurity compliance involves adhering to a set of laws, regulations, and standards designed to protect digital assets and data. These frameworks ensure organizations implement adequate security controls, manage risks effectively, and maintain data integrity, confidentiality, and availability. Achieving compliance minimizes legal repercussions and strengthens an organization's overall security posture.
Key Points
-
Compliance Mitigates Risk
Cybersecurity compliance is a proactive risk management tool that not only helps avoid penalties but ultimately builds trust. -
Frameworks Are Essential
Understanding and implementing compliance frameworks, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and NIST CSF, is essential for organizations to maintain a comprehensive security posture. -
Compliance is Continuous
Compliance isn't merely a checklist exercise; it's a continuous process that requires ongoing training, technological solutions, and policy enforcement. -
People, Process, Tech
The three pillars of cybersecurity compliance—people, process, and technology—must work in concert to build a comprehensive and resilient security environment. -
AI Transforms Compliance
Emerging trends, including the impact of AI on compliance automation and the growing emphasis on third-party risk management, are shaping the future of cybersecurity compliance.
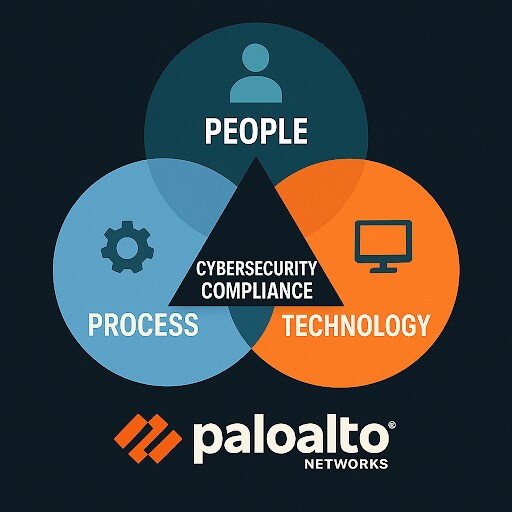
Understanding Cybersecurity Compliance
Cybersecurity compliance is crucial for safeguarding an organization's information systems and sensitive data. It isn't just about avoiding penalties—it's a fundamental aspect of effective risk management and building trust with customers and partners. By adhering to established guidelines, businesses can proactively defend against evolving cyberthreats.
Compliance frameworks offer a structured approach to cybersecurity, enabling organizations to identify vulnerabilities and implement necessary controls. This systematic process ensures that security measures are not only in place but also regularly reviewed and updated to meet current threat landscapes.
Ultimately, a strong compliance posture signals a commitment to data protection and operational integrity, which are vital in today's digital economy.
| Framework Name | Primary Scope | Key Requirements | Applicability |
|---|---|---|---|
| HIPAA | Patient health information |
|
Healthcare organizations, Business associates |
| PCI DSS | Cardholder Data |
|
Any entity processing, storing, or transmitting credit card data |
| GDPR | Personal Data of EU Citizens |
|
Any organization processing personal data of EU residents |
| NIST CSF | Cybersecurity Risk Management |
|
All organizations, voluntary |
| ISO/IEC 27001 | Information Security Management |
|
All organizations, international |
Key Security Compliance Frameworks and Regulations
Organizations navigate a complex landscape of compliance frameworks, each designed to address specific industry or data protection requirements. Understanding these diverse regulations is critical for achieving and maintaining cybersecurity compliance. Failure to comply can result in significant financial penalties, legal action, and reputational damage.
Industry-Specific Regulations
Different industries face unique compliance obligations tailored to the sensitive data they handle. Adhering to these sector-specific mandates helps protect consumer information and maintain public trust.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): U.S. law that governs the protection of sensitive patient health information (PHI) by requiring healthcare organizations and their business associates to implement administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of PHI.
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): Not a law, but a set of security standards mandated by major credit card brands for entities that process, store, or transmit cardholder data. PCI DSS aims to reduce credit card fraud by enforcing strict security controls around payment card information.
- CMMC (Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification): Developed by the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD), CMMC is a tiered certification model for defense contractors and their supply chain. It assesses and certifies a contractor's ability to protect Federal Contract Information (FCI) and Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI).
Global and Regional Data Protection Laws
The proliferation of data across borders has led to the development of comprehensive data protection laws that apply to a broad range of organizations. These regulations emphasize individual privacy rights and impose strict requirements on data handling.
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): This European Union law sets strict rules on how personal data of EU citizens is collected, processed, stored, and transferred. GDPR applies to any organization, anywhere in the world, that processes data of EU residents. It grants individuals significant rights over their personal data.
- CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act): A landmark U.S. state law that grants California consumers extensive rights regarding their personal information. CCPA requires businesses to be transparent about data collection practices and provides consumers with the right to access, delete, and opt out of the sale of their personal data.
Foundational Cybersecurity Frameworks
Beyond specific regulations, several widely adopted cybersecurity frameworks provide a comprehensive approach to managing cybersecurity risks. These frameworks offer best practices that organizations can adapt to their unique environments.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF): Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) provides a flexible, voluntary framework for organizations to manage and mitigate cybersecurity risks. It consists of five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover.
- ISO/IEC 27001: An international standard for information security management systems (ISMS). ISO 27001 provides a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information so it remains secure. It includes a process for assessing and treating information security risks.
- CIS Controls (Center for Internet Security Critical Security Controls): A prioritized set of actions that form a defense-in-depth for cyber protection. The CIS Controls are recognized globally as a foundational set of best practices in cybersecurity.
Building an Effective Cybersecurity Compliance Program
Establishing a comprehensive cybersecurity compliance program requires a systematic approach that integrates various elements to ensure ongoing adherence to regulations and best practices. It involves more than just a one-time audit—it's a continuous journey.
Key Components of a Compliance Program
An effective compliance program relies on several interconnected components, from foundational policies to continuous monitoring. Each element plays a vital role in maintaining a strong security posture.
Policy Development and Enforcement
Organizations must develop clear, comprehensive cybersecurity policies that align with relevant compliance frameworks. These policies should encompass areas such as data handling, access control, incident response, and employee training and education. Consistent enforcement of these policies is critical to their effectiveness.
Risk Assessment and Management
Regular and thorough risk assessments are fundamental to identifying vulnerabilities and threats. This process enables organizations to understand their unique risk profile and prioritize effective mitigation strategies. Effective risk management involves continuous monitoring and adaptation to new threats.
Security Controls Implementation
Translating policies and risk assessments into actionable security controls is essential. This includes implementing technical measures like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption, and multifactor authentication. Physical security controls and administrative controls are also vital.
Employee Training and Awareness
Human error remains a significant factor in many security incidents. Comprehensive security awareness training for all employees is paramount. This training should cover topics such as phishing, social engineering, data handling best practices, and incident reporting procedures.
Continuous Monitoring and Auditing
Compliance is not a static state; it requires ongoing vigilance and attention. Continuous monitoring of systems and processes helps detect deviations from policy and potential security breaches. Regular internal and external audits verify the effectiveness of compliance and identify areas for improvement.
Overcoming Common Compliance Challenges
Organizations frequently encounter hurdles when striving for and maintaining cybersecurity compliance. Anticipating these challenges can help in developing more resilient compliance strategies.
Limited Resources
Many organizations, particularly small to medium-sized businesses, struggle with insufficient budget, staff, or expertise to manage complex compliance requirements. Prioritizing critical controls and leveraging automated tools can help mitigate this.
Evolving Threat Landscape
Cyber threats are constantly changing, making it difficult for organizations to keep pace with new attack vectors and vulnerabilities. Continuous threat intelligence gathering and agile security practices are necessary to stay ahead.
Complexity of Regulations
The sheer volume and complexity of overlapping compliance frameworks can be overwhelming. Mapping controls across multiple frameworks can help streamline efforts and reduce redundant work.
Lack of Leadership Buy-in
Without strong support from senior leadership, compliance initiatives may lack the necessary funding and organizational priority. Demonstrating the business value of compliance, beyond avoiding penalties, can foster better buy-in.
Managing Third-Party Risk
As supply chains become more interconnected, managing the cybersecurity compliance of third-party vendors and partners is increasingly challenging. Comprehensive vendor risk management programs are crucial for addressing this.
The Future of Cybersecurity Compliance: AI and Emerging Trends
The landscape of cybersecurity compliance is dynamic, continually evolving in response to technological advancements and shifting regulatory demands. Artificial intelligence (AI) is emerging as a powerful tool for enhancing compliance efforts, while new trends redefine how organizations approach security.
Impact of AI on Compliance
AI is poised to revolutionize how organizations manage and maintain cybersecurity compliance, offering capabilities that far surpass traditional methods. These advancements will make compliance processes more efficient and proactive.
Automated Compliance Monitoring
AI-powered systems can continuously monitor networks, endpoints, and data flows for compliance deviations in real time. This automation significantly reduces the manual effort required for audits and ensures consistent adherence to policies.
Predictive Analytics for Risk Assessment
AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets of threat intelligence, vulnerability reports, and historical incident data to predict potential compliance risks. This predictive capability enables organizations to address vulnerabilities before they are exploited, allowing them to act proactively and effectively.
Enhanced Anomaly Detection
AI excels at identifying unusual patterns and anomalies in user behavior and system activity that may indicate policy violations or data breaches. This capability strengthens detective controls and accelerates incident response.
Streamlined Audit Processes
AI can automate the collection and analysis of evidence required for audits, significantly reducing the time and resources spent on compliance reporting. This results in faster audit cycles and enhanced accuracy.
Emerging Trends in Cybersecurity Compliance
Beyond AI, several other trends are shaping the future of cybersecurity compliance, reflecting a growing emphasis on proactive defense, integrated risk management, and accountability. These shifts will drive the development of new strategies for protecting digital assets.
Shift Towards Proactive Compliance
The focus is moving from reactive, audit-driven compliance to a proactive, continuous approach. This involves integrating security and compliance into every stage of the software development lifecycle and business operations.
Increased Emphasis on Third-Party Risk Management
With supply chain attacks on the rise, organizations are scrutinizing the cybersecurity compliance of their vendors and partners more rigorously. This involves comprehensive due diligence and continuous monitoring of third-party security postures.
Data Privacy as a Core Compliance Element
Global data privacy regulations continue to expand, making privacy a central component of cybersecurity compliance. Organizations must implement resilient privacy-by-design principles and comprehensive data governance.
Compliance Automation and Orchestration
Tools that automate compliance tasks and orchestrate security controls are becoming indispensable. These solutions help manage the complexity of multiple frameworks and reduce the potential for human error.
Cyber Insurance Requirements
Insurers are increasingly demanding higher levels of cybersecurity compliance as a prerequisite for coverage. This trend incentivizes organizations to enhance their security measures to qualify for and maintain cyber insurance policies.