- What Is Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI)?
- Threat Intelligence Use Cases and Examples
-
What is a Threat Intelligence Platform (TIP)?
- The Value of a Threat Intelligence Platform
- How Threat Intelligence Works
- Types and Examples of Threat Intelligence
- Why Do Organizations Need a Threat Intelligence Platform (TIP)?
- Key Characteristics of a Threat Intelligence Platform
- Types of Threat Intelligence Data
- Implementation of a Threat Intelligence Platform
- Threat Intelligence Platforms FAQs
- What Are Unknown Cyberthreats?
- What Are Cyberthreat Intelligence Tools?
- What are the Types of Cyberthreat Intelligence (CTI)?
What is the Threat Intelligence Lifecycle?
The threat intelligence lifecycle is a process used in cybersecurity to manage cyberthreats. It helps organizations protect their information assets by gathering, analyzing, and applying information about potential and current cyberthreats. The goal is continuously improving the quality and relevance of threat intelligence, adapting to the evolving cyberthreat landscape.
The cycle typically consists of these stages:
- Direction/Discovery: Aims to identify or discover consumers' intelligence requirements.
- Collection: Data and information are collected from various sources to meet the identified requirements.
- Processing: Data is cleaned to remove duplicates, inconsistencies, and irrelevant information, transformed into a format suitable for analysis, and enhanced with additional context and metadata.
- Analysis: Raw data and information are collated, fused with other sources, and turned into intelligence with various machine and human techniques.
- Dissemination/Action: The timely conveyance of completed intelligence products is distributed appropriately to the intended consumers.
- Feedback: Ongoing assessment of the effectiveness of each step of the intelligence cycle to ensure the best possible intelligence reaches the intended consumer.
Why is the Threat Intelligence Lifecycle Important?
The threat intelligence lifecycle is a continuous and evolving process that assists organizations in staying ahead of cyberthreats by constantly improving their comprehension of the threat landscape and adjusting their defenses accordingly.
By concentrating on pertinent threats, the lifecycle reduces the impact of attacks, enabling organizations to respond more effectively and maintain a robust and adaptable cybersecurity posture.
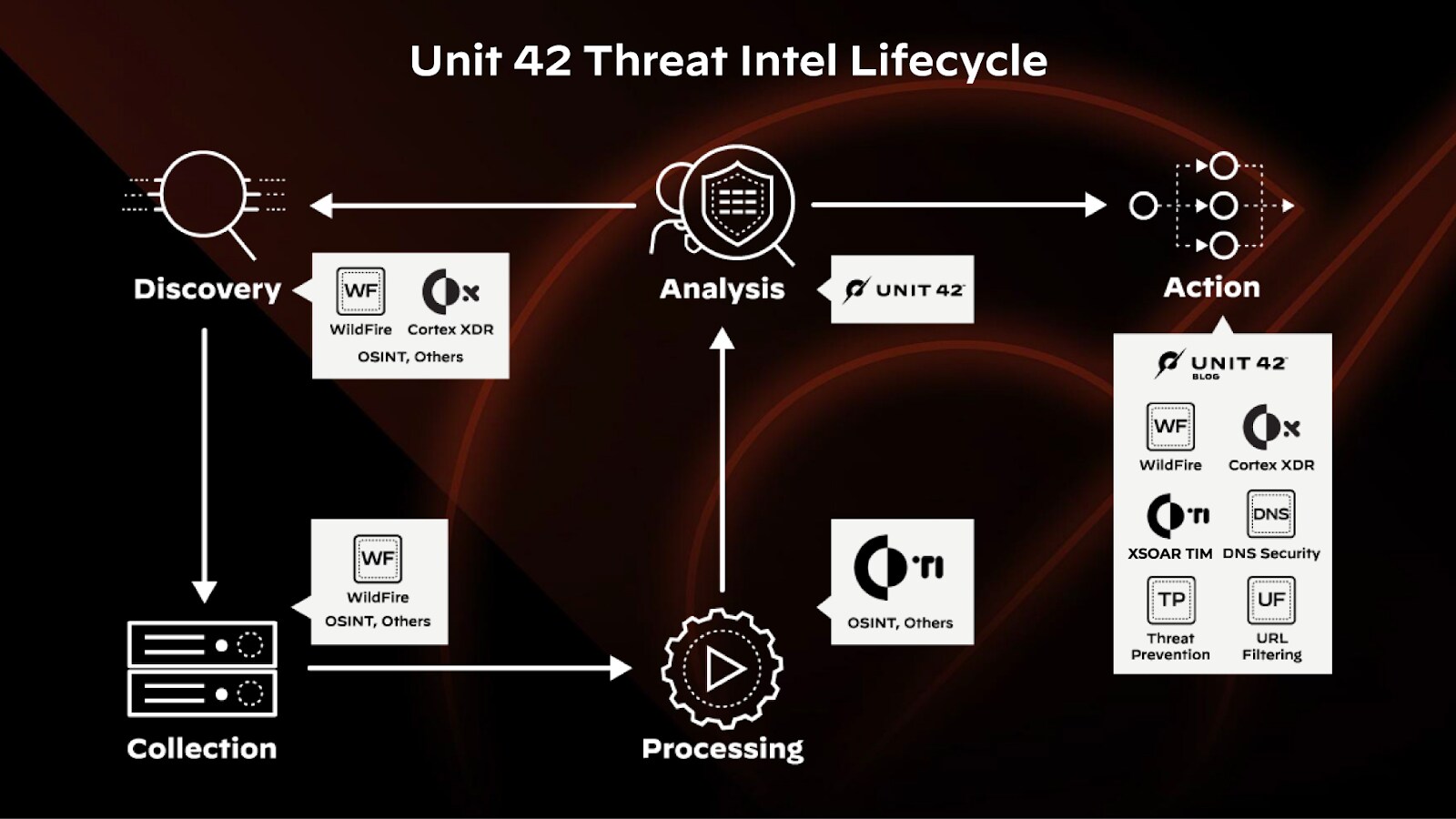
The 6 Stages of the Threat Intelligence Lifecycle
The threat intelligence process involves six connected stages that work together to gather, analyze, and disseminate information about potential threats. This iterative process uses feedback from each stage to refine subsequent strategies, continuously improving the organization's ability to identify and respond to threats.
Direction/Discovery
To initiate the lifecycle, security teams collaborate with business stakeholders to define the threat intelligence program's objectives and goals. This often starts with determining what assets and data need protection, allocating resources and budget, and establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the program's success. This phase is an essential starting point because it creates the basis for the entire threat intelligence process.
Collection
During the collection phase, organizations gather data and information from various sources identified during the Direction phase, including:
- Internal logs
- External threat feeds
- Open-source intelligence (OSINT)
- Information sharing and analysis centers (ISACS)
- SOCMINT
- Government agencies, industry groups, and commercial vendors
- Deep and dark web intelligence
Processing
Collected data is transformed into a format that can be easily analyzed. The processing step includes sorting, decrypting, and translating the data into a usable form. Sorting the data involves organizing it into categories or groups based on specific criteria. Data is decrypted, decoding any encrypted or coded data to be read and understood.
Last, data is translated and converted from one language or format into another, making it easier to comprehend and interpret. This significant step enables analysts to work more effectively and efficiently with the data.
Analysis
When analyzing data for potential cyberthreats or attacks, experts examine the processed data to pinpoint patterns, anomalies, and other signs of malicious activity. This process often involves cross-referencing data from various sources and using analytical techniques to understand the context and implications of the information.
Dissemination/Action
The analyzed intelligence is distributed to the intended audience. This could be decision-makers within the organization, operational teams, or external partners. The key is to ensure that the intelligence is presented in an actionable and relevant way.
Feedback
Gathering feedback from key stakeholders on the efficacy and pertinence of the offered threat intelligence is a crucial step in enhancing and refining the threat intelligence process. The feedback received from the stakeholders is meticulously analyzed to identify gaps in the intelligence process and areas that require improvement and to ensure that the provided intelligence is relevant and up-to-date. The insights gleaned from the feedback are used to refine and improve the threat intelligence process, enabling the deliverance of more targeted and better intelligence to our stakeholders.
Benefits of the Threat Intelligence Lifecycle Framework
The threat intelligence lifecycle enhances an organization's ability to defend against cyberthreats and contributes to a more strategic, efficient, and comprehensive approach to managing cybersecurity risks. Potential benefits include:
- Detecting and responding to potential threats early can significantly reduce the impact of cyberattacks.
- Managing cybersecurity risks more strategically by understanding the evolving threat landscape and allocating resources for maximum impact.
- Saving costs by proactively preventing attacks or mitigating their impact, rather than dealing with the aftermath of a cyberattack.
- Strengthening security measures and making them more resilient against cyberattacks.
- Providing valuable context for incident response and forensic analysis in a security breach.
- Gaining a competitive advantage by effectively managing cyberthreats and being seen as more reliable and secure by customers and business partners.
- Developing tailored security solutions that address specific vulnerabilities.
- Obtaining a broader perspective on cyberthreats by incorporating information from various global sources.
- Fostering a culture of security awareness by integrating threat intelligence into an organization's operations, encouraging employees to be more vigilant and understand the importance of cybersecurity in their roles.
