- 1. What Is an SWG?
- 2. What Is a Proxy Server?
- 3. Is a Proxy and Secure Web Gateway the Same?
- 4. What Are the Differences Between SWGs and Proxy Servers?
- 5. What Are the Similarities Between SWGs and Proxy Servers?
- 6. How to Choose Between SWG vs. Proxy Server
- 7. The Roles of SWGs and Proxy Servers in SASE
- 8. SWG vs. Proxy Server FAQs
- What Is an SWG?
- What Is a Proxy Server?
- Is a Proxy and Secure Web Gateway the Same?
- What Are the Differences Between SWGs and Proxy Servers?
- What Are the Similarities Between SWGs and Proxy Servers?
- How to Choose Between SWG vs. Proxy Server
- The Roles of SWGs and Proxy Servers in SASE
- SWG vs. Proxy Server FAQs
Secure Web Gateway vs. Proxy Server: What Is the Difference?
- What Is an SWG?
- What Is a Proxy Server?
- Is a Proxy and Secure Web Gateway the Same?
- What Are the Differences Between SWGs and Proxy Servers?
- What Are the Similarities Between SWGs and Proxy Servers?
- How to Choose Between SWG vs. Proxy Server
- The Roles of SWGs and Proxy Servers in SASE
- SWG vs. Proxy Server FAQs
The difference between an SWG) and proxy server is that an SWG is a complete web traffic security solution that enforces policies and protects against threats, while a proxy server is an intermediary for web requests.
An SWG offers advanced security features like malware scanning, URL filtering, and content inspection, which enhances network security. A proxy server typically focuses on IP address concealment and content caching, providing basic security without advanced features.
SWGs allow for granular policy enforcement and control based on user identity, device, and location, ensuring regulatory compliance and acceptable use policies. In contrast, since proxies can only inspect web-based traffic, they are typically part of a more comprehensive security platform strategy.
What Is an SWG?
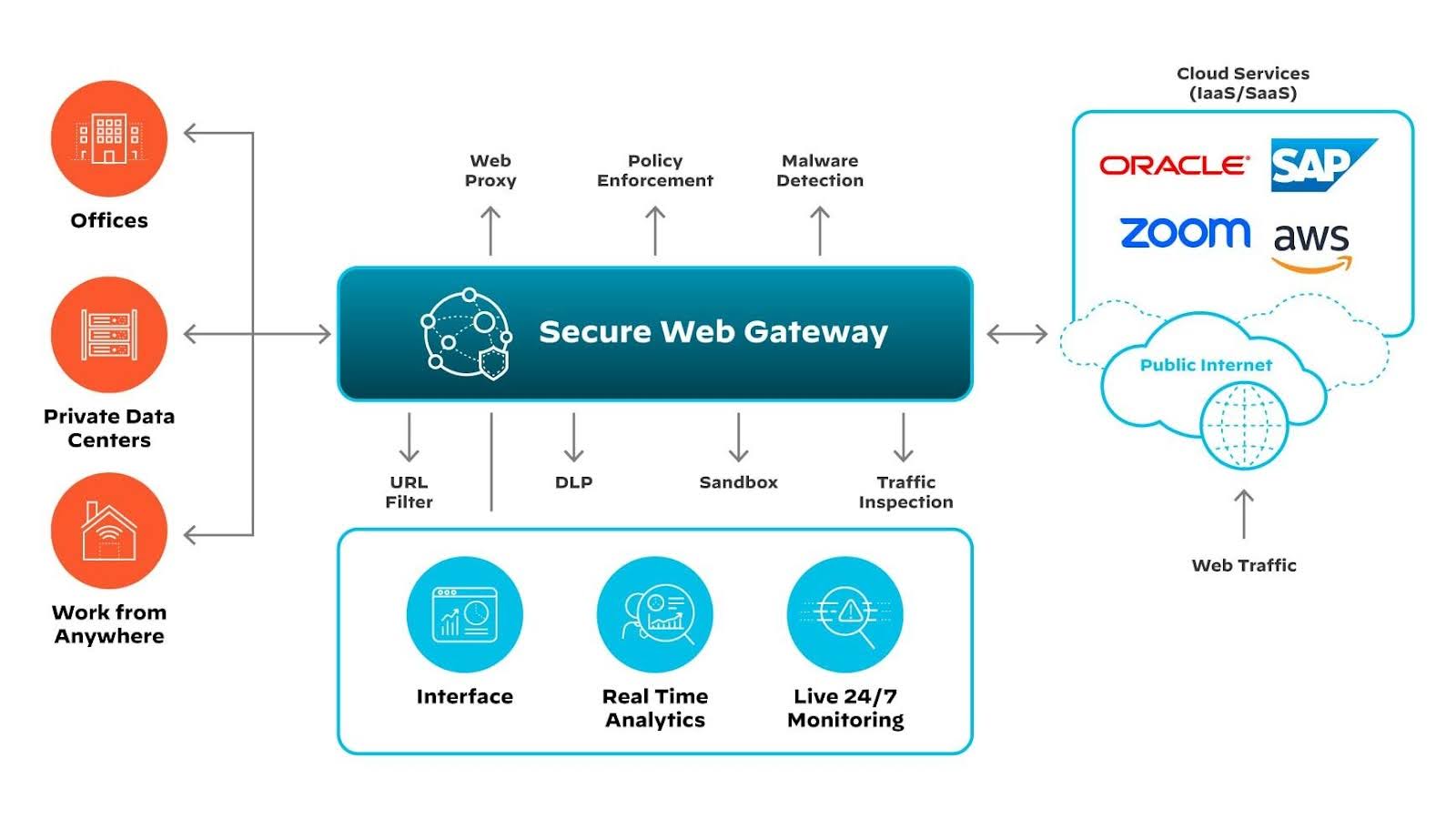
An SWG is a cybersecurity solution that acts as an intermediary between end-user devices and the internet to enforce data policy compliance and protect against online threats.
Secure web gateways are critical for modern internet security. They inspect and control web traffic to and from an organization's network, blocking what’s malicious and ensuring sensitive information does not leave the secured perimeter. By analyzing data in real time, SWGs prevent various online threats, like malware or phishing attacks, from compromising the network.
The traffic inspection process involves various security features like URL filtering, application controls, and antimalware protocols. Each time a user attempts to access the web, the SWG checks the request against these security measures. If the SWG deems the request as safe, it allows the request; if not, the SWG blocks it to prevent potential harm to the organization's network.
By deploying an SWG, organizations can significantly reduce exposure to internet-based risks. This is increasingly important as businesses adopt cloud services and support a mobile workforce, which can introduce new vulnerabilities. A robust SWG ensures threat protection and secure internet use, which is vital to maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive data.
What Is a Secure Web Gateway (SWG)?
What Is a Proxy Server?
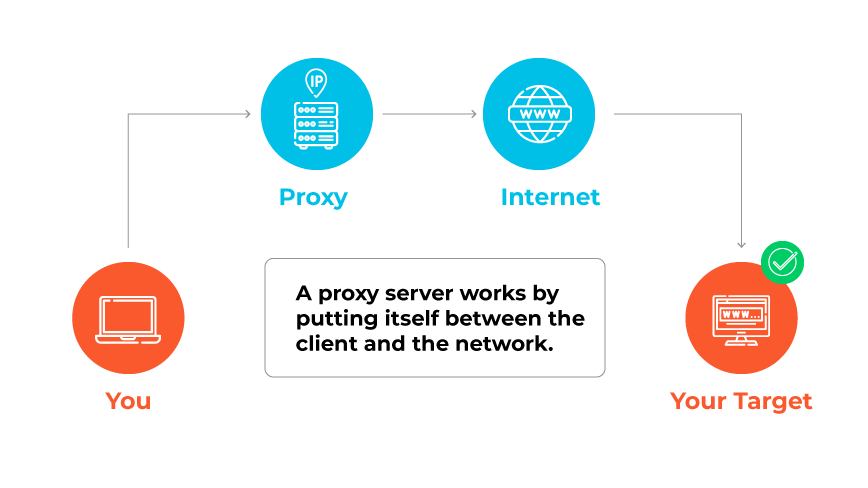
A proxy server is a server that acts as an intermediary between a user’s device and the internet, directing online requests and responses to maintain privacy and security.
Proxy servers serve as a middleman in the communication between end users and the services or websites they wish to access. When a device connects to the internet through a proxy, the proxy makes web requests on behalf of the device, receives the response, and forwards it back to the user. This process hides the user's IP address, which can provide anonymity and protect against network attacks.
Proxy servers can also perform additional functions like content caching to improve load times for frequently accessed resources. They can enforce organizational access policies and restrict access to websites that aren’t approved, enhancing security and productivity. Proxy configuration options can allow for encrypted connections, adding a layer of security for data in transit.
Is a Proxy and Secure Web Gateway the Same?
SWGs and proxy servers aren’t the same thing. A proxy is a networking function, while an SWG is a comprehensive security solution. When the security market initially categorized secure web gateways, web proxy vendors offered many of the solutions.
A secure web gateway does work similarly to a traditional proxy in that it serves as an intermediary between client devices and web servers. For example, when a user requests a webpage, the SWG intercepts the request, fetches the page from the server, and delivers it to the user.
However, an SWG surpasses basic proxy capabilities by incorporating advanced security measures, including malware detection, URL filtering, and content inspection.
What Are the Differences Between SWGs and Proxy Servers?
| Web Security Gateway vs. Proxy Server: What Are the Differences? | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameters | SWG | Proxy Server |
| Functionality | Comprehensive security solution filtering internet traffic, enforcing policies, and ensuring compliance. | Intermediary for web requests, providing anonymity and content caching. |
| Security Capabilities | Advanced features like data loss prevention (DLP), malware scanning, URL filtering, and content inspection. | Basic security, offering IP address concealment and content caching. |
| Policy Enforcement and Control | Granular policy control based on user identity, device, and location. | Primarily used for anonymous browsing and content filtering, lacks granular control. |
| Deployment and Architecture | Can be deployed as on-premises appliances or cloud-delivered services. | Typically deployed as standalone servers or software applications. |
Functionality
Secure web gateways and proxy servers serve distinct functions within a network. A proxy server is an intermediary between a user's device and the internet, rerouting traffic and concealing the user's IP address.
In contrast, an SWG is a comprehensive security solution that filters internet traffic, enforces security policies, and ensures regulatory compliance. While both technologies mediate internet traffic, an SWG offers advanced security features beyond basic proxy functionality.
Security Capabilities
One of the primary differences between SWGs and proxy servers is security capabilities. SWGs provide advanced security features such as malware scanning, URL filtering, and content inspection, enhancing network security. Proxy servers do not typically provide the same level of comprehensive security features as SWGs.
Policy Enforcement and Control
SWGs allow organizations to enforce security policies and control access to web content based on user identity, device, and location. This granular control ensures organizations can enforce acceptable use policies and maintain regulatory compliance. Proxy servers, on the other hand, do not offer the same level of policy enforcement and control capabilities.
Deployment and Architecture
SWGs and proxy servers also differ in deployment and architecture. SWGs offer flexible deployment options, including on-premises appliances or cloud-based services. Proxy servers are typically deployed as standalone servers or software applications, often requiring individual configurations for each application.
What Are the Similarities Between SWGs and Proxy Servers?
| Secure Web Gateway vs. Proxy Server: What Are the Similarities? | |
|---|---|
|
|
Traffic Management
Both SWGs and proxy servers act as intermediaries between users and the internet, intercepting and managing traffic requests. They serve as gateways for outgoing requests, inspecting and filtering traffic based on predefined policies and rules. This intermediary role allows them to enforce security measures and control access to internet resources.
Caching Capabilities
Both technologies can cache frequently accessed web content, improving performance by reducing the need to retrieve data from the internet for subsequent requests. By storing copies of webpages locally, SWGs and proxy servers can provide faster access to content, especially for websites with high traffic volume.
Anonymity and Privacy
SWGs and proxy servers can enhance user anonymity and privacy by masking the user's IP address, making it appear as though the traffic originates from the proxy server or SWG.
Access Control and Filtering
Both SWGs and proxy servers enable access control and content filtering. They can block access to websites or categories of websites based on predefined policies. This capability allows organizations to enforce acceptable use policies and protect users from accessing malicious or inappropriate content.
How to Choose Between SWG vs. Proxy Server
Choosing between SWG and a proxy server depends on specific needs.
If an organization requires enhanced security, particularly for network and data security, an SWG is the better choice. While a proxy can offer browser anonymity and faster network performance, it may not provide the comprehensive security measures necessary for robust protection.
However, if the primary concern is browser anonymity or improving network performance without the need for extensive security measures, a proxy may be sufficient.
The Roles of SWGs and Proxy Servers in SASE
Organizations should consider the SWG as a fundamental component leading to a unified, comprehensive SSE/SASE platform. Consolidated solutions provide centralized policy management, allowing security teams to oversee operations more efficiently. Choose a vendor offering a single SASE solution, encompassing FWaaS, CASB, SWG, ZTNA, and SD-WAN within a unified security platform.
The same can be said for proxies. Organizations can achieve a balance between architectural flexibility and security by integrating proxies into a secure access service edge (SASE) approach. SASE solutions offer comprehensive networking and security features in a unified cloud-based service, ensuring optimal security while accommodating diverse networking needs.